Structural Unemployment Graph Explanation
As individual firms demand falls the firm decreases its output. Structural unemployment is a longer-lasting form of unemployment caused by fundamental shifts in an economy and exacerbated by extraneous factors such as technology competition and government policy.
 Structural Unemployment Definition Causes And Graph
Structural Unemployment Definition Causes And Graph
Long-term chronic unemployment that exists when the economy is not in a recessionThe main causes of structural unemployment are.

Structural unemployment graph explanation. Go to selected chart. However it is not always an indicator of a recession Deflation Deflation is a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. Labor markets since the late 90screated a skill.
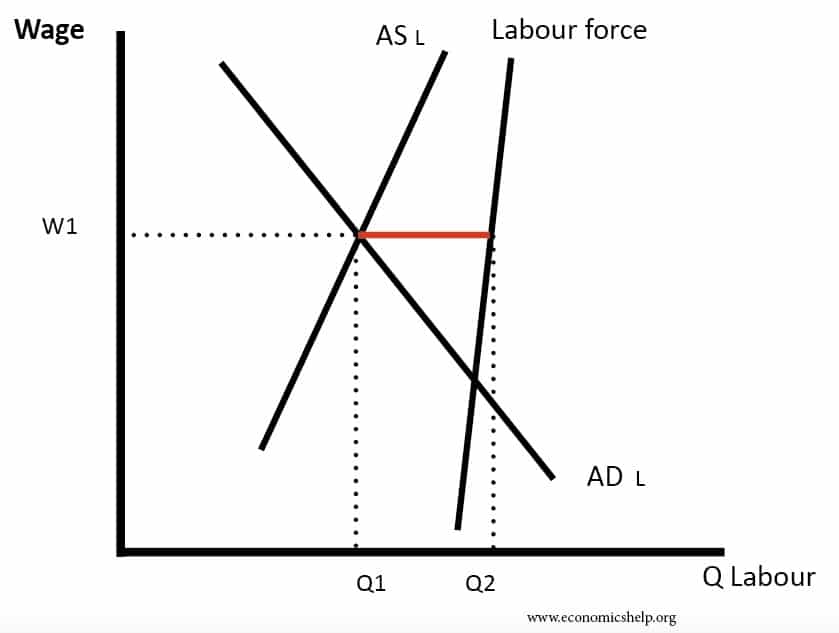
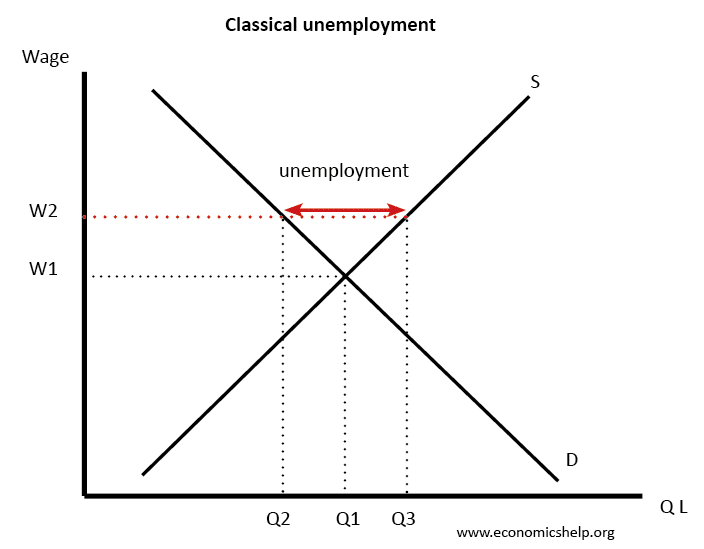
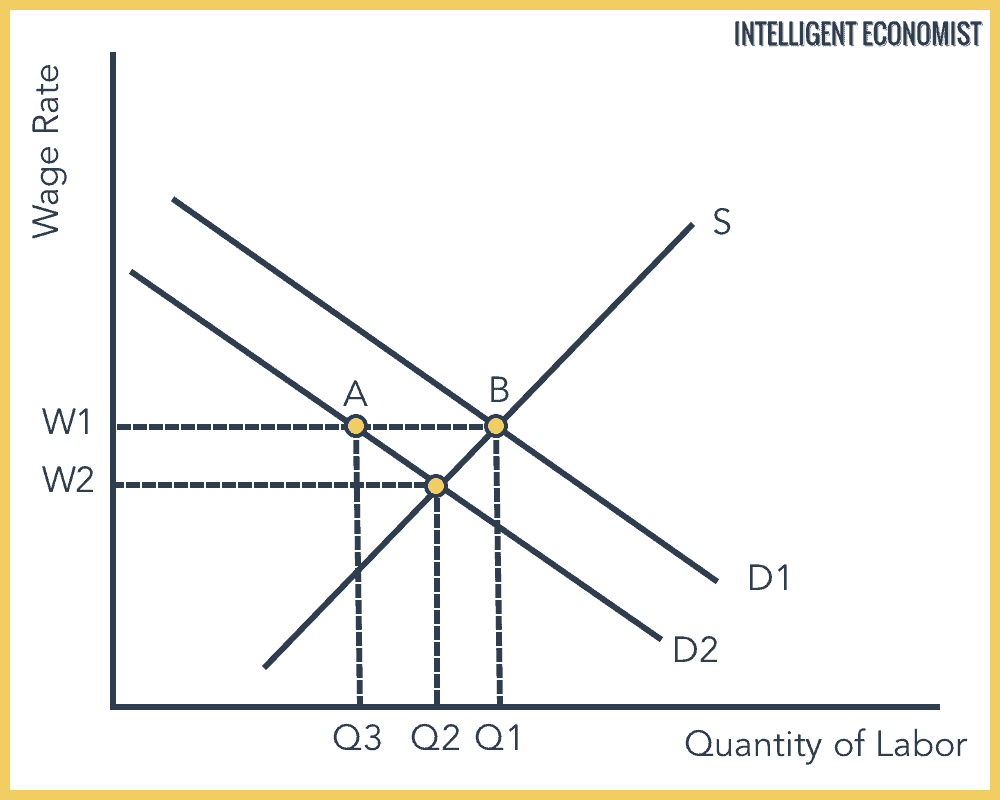
Frictional unemployment is due to voluntary unemployment when looking for a different job. Hence the demand for labour decreases D1 - D2. Structural unemployment results from inability of labor market to arrive at the market-clearing wage at which the number of workers are just equal to the number of jobs.
Structural unemployment comes about through technological change in the structure of the economy in which labor markets operate. Structural Unemployment Definition. Structural unemployment is attributed to a less qualified workforce.
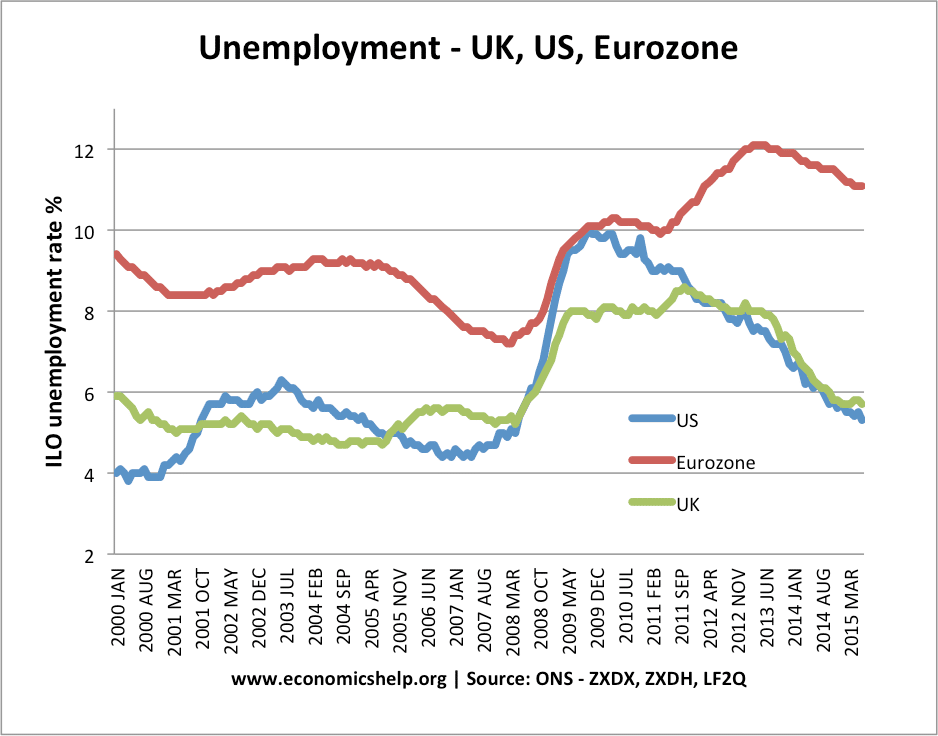
The graph also shows higher structural unemployment in the Eurozone. Oxford UK 21st September 2017. On the Labour force diagram cyclical demand deficient unemployment can be shown as follows.
Even during times of growth the average unemployment rate is higher. Structural unemployment is the unemployment that exists when wages do not adjust to equilibrium such that the number of job-seekers exceed the number of available jobs even in an economic boom. This type of unemployment happens because though jobs are available theres a.
Because wages do not fall there appears an unemployment of amount Q1-Q2 the distance between D1 and D2 at wage W1. Structural unemployment u s occurs when at the prevailing wage there is a surplus of workers and the market is not able to reach equilibrium due to wage rigidity. 1 It occurs when an underlying shift in the economy makes it.
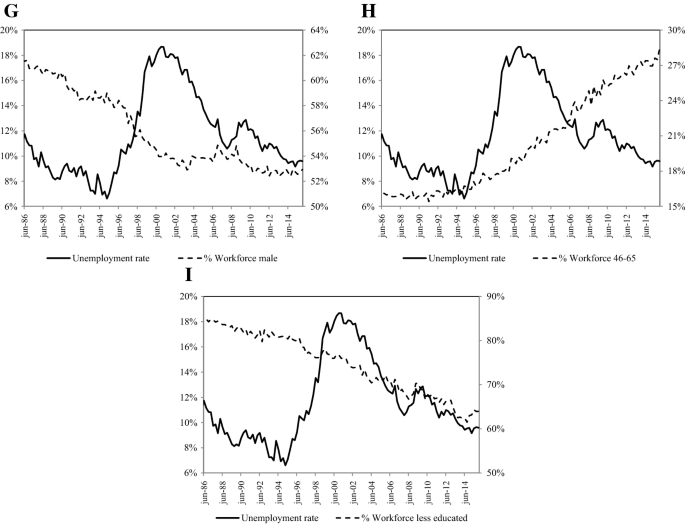
It can result in an increase in the natural unemployment rate. Even when there is plenty of job availability this mismatch means that the unemployed cannot access jobs that fit their skill sets. Structural unemployment refers to a mismatch between the jobs available and the skill levels of the unemployed.
Technological changessuch as the replacement of. 1 the number of low skilled workers. Unemployment definitions and statistics Types of Unemployment.
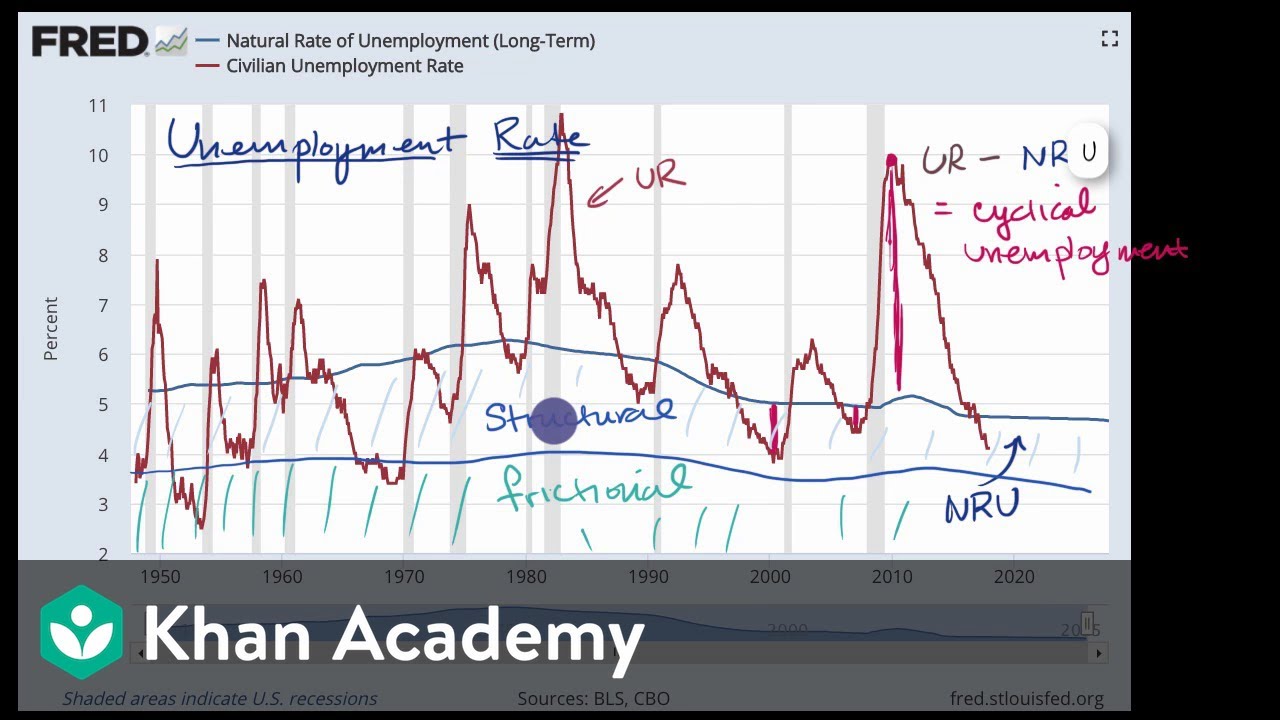
This structural unemployment has been attributed to factors such as labour market immobilities and excessive labour market regulation. Structural unemployment is a significant problem in economics because of its long-lasting effects and challenges associated with overcoming the issue. It follows that the actual unemployment rate is the sum of rate of frictional unemployment rate of structural unemployment and rate of cyclical unemployment.
Definition Causes Solution Explanations. Structural Unemployment Structural unemployment occurs when there is a mismatch between the jobs that are available and the people looking for work. This mismatch could be because jobseekers dont have the skills required to do the available jobs or because the.
Unlike cyclical unemployment its caused by forces other than the business cycle. I demonstrate that the decline in routine-cognitive jobs outside manufacturinga pervasive structural change that has affected US. 242 rows Unemployment National Unemployment Rate.
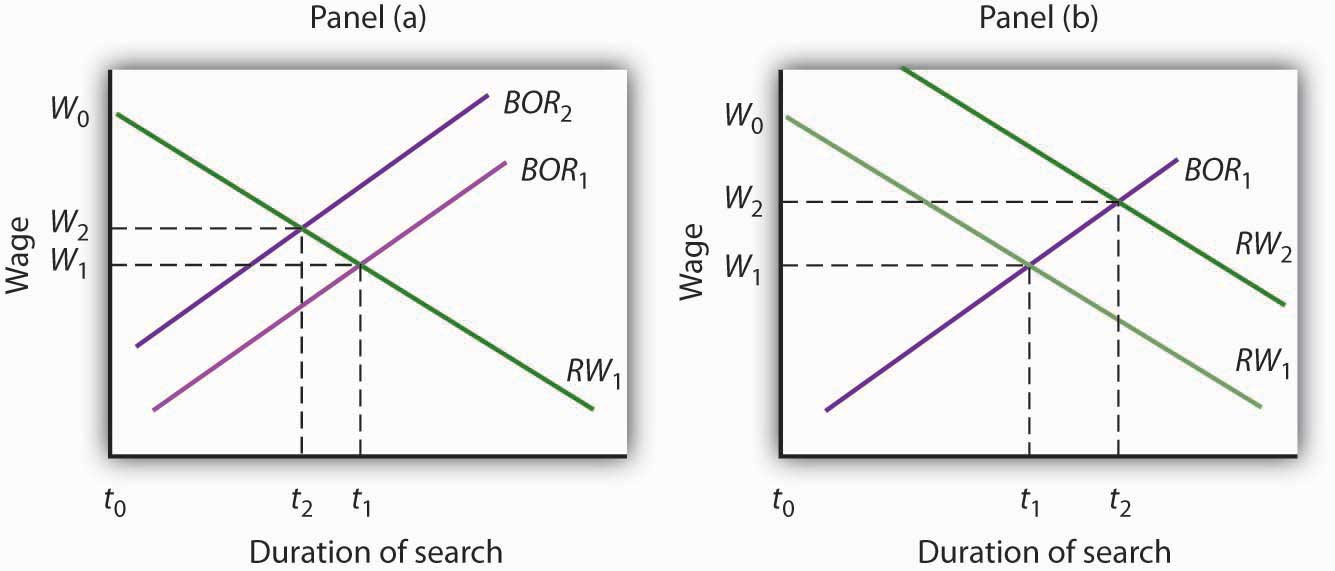
Moreover structural change interacts with the business cycle causing a large and long-lasting increase in unemployment that concentrates in recessions. Structural unemployment results from mismatches between the skills required for available jobs and the skills held by the unemployed. Put another way deflation is negative inflation.
Structural unemployment occurs because workers lack the requisite job skills or workers live too far from regions where jobs are available and cannot. Seasonal unemployment occurs when seasonal workers are unemployed and classical unemployment is when wages are too high and companies cannot afford to pay them. Unemployment caused by workers searching for jobs and firms searching for workers.
Exists when there are jobs available and people willing to do work but there are not a. Structural unemployment is long-lasting unemployment that comes about due to shifts in an economy.
 The Natural Rate Of Unemployment Economics Help
The Natural Rate Of Unemployment Economics Help
 31 3 Inflation And Unemployment In The Long Run Principles Of Economics
31 3 Inflation And Unemployment In The Long Run Principles Of Economics
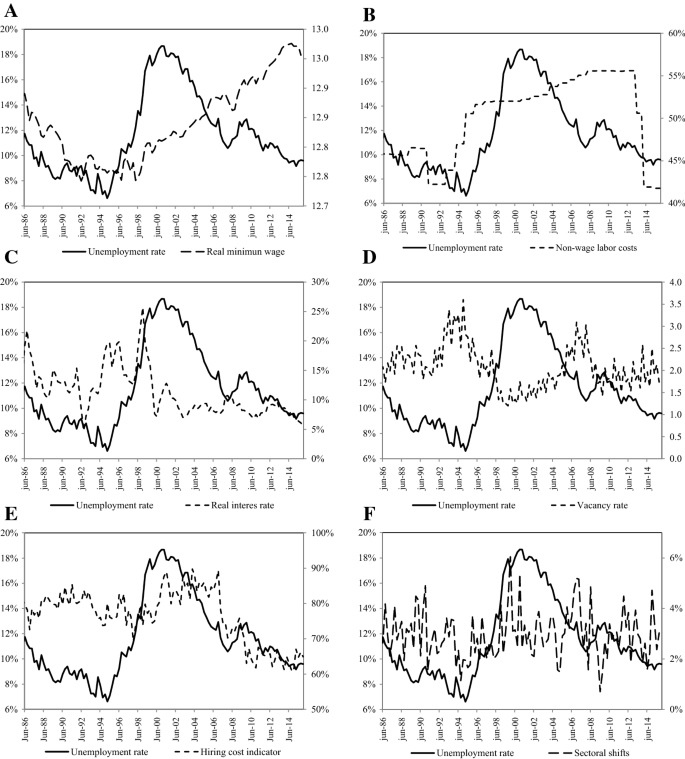
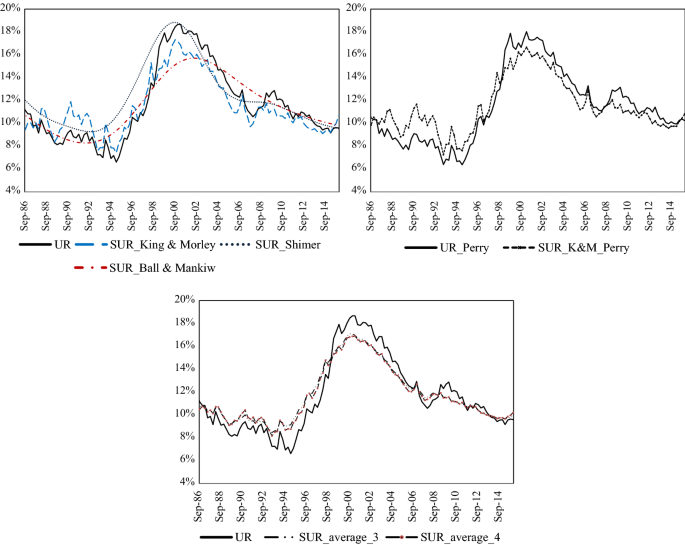
 Determinants Of Structural Unemployment In Colombia A Search Approach Springerlink
Determinants Of Structural Unemployment In Colombia A Search Approach Springerlink
 Hypercompetition Characteristics Basic Concepts Encouragement Finance
Hypercompetition Characteristics Basic Concepts Encouragement Finance
 The Natural Rate Of Unemployment Economics Help
The Natural Rate Of Unemployment Economics Help
 Real Wage Unemployment Economics Help
Real Wage Unemployment Economics Help
 Natural Cyclical Structural And Frictional Unemployment Rates Video Khan Academy
Natural Cyclical Structural And Frictional Unemployment Rates Video Khan Academy
 Causes Of Unemployment In The United States Wikipedia
Causes Of Unemployment In The United States Wikipedia
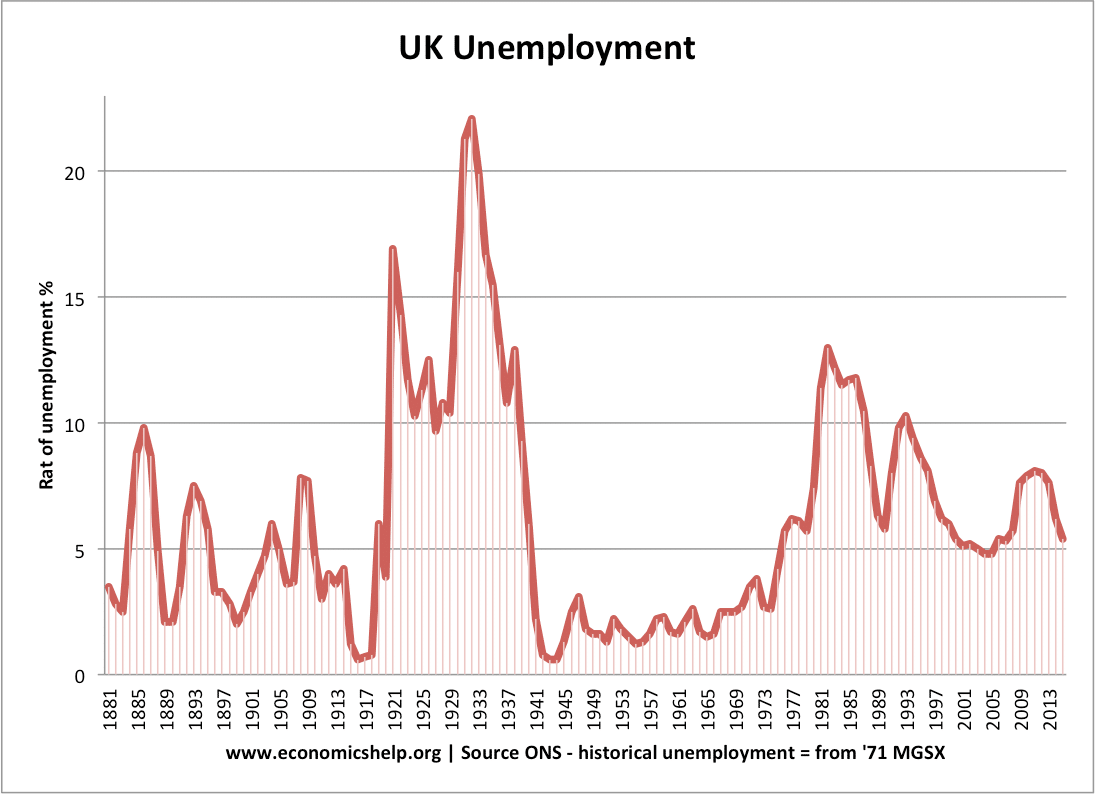
 Structural Unemployment Economics Help
Structural Unemployment Economics Help
/UnemploymentandGDP2008-80ffa8c6bee640208888f8cc26cb38e2.jpg) Unemployment And Recession What S The Relation
Unemployment And Recession What S The Relation
 Determinants Of Structural Unemployment In Colombia A Search Approach Springerlink
Determinants Of Structural Unemployment In Colombia A Search Approach Springerlink
 Cyclical Unemployment Intelligent Economist
Cyclical Unemployment Intelligent Economist
 Structural Unemployment Economics Help
Structural Unemployment Economics Help
Ib Economics Unemployment Notes On Unemployment
Ib Economics Unemployment Notes On Unemployment
 Determinants Of Structural Unemployment In Colombia A Search Approach Springerlink
Determinants Of Structural Unemployment In Colombia A Search Approach Springerlink
Ib Economics Unemployment Notes On Unemployment
Post a Comment for "Structural Unemployment Graph Explanation"