German Unemployment Rate Great Depression
The German unemployment rate rose to just 4 percent that month. Unemployment Great Depression in the United States.
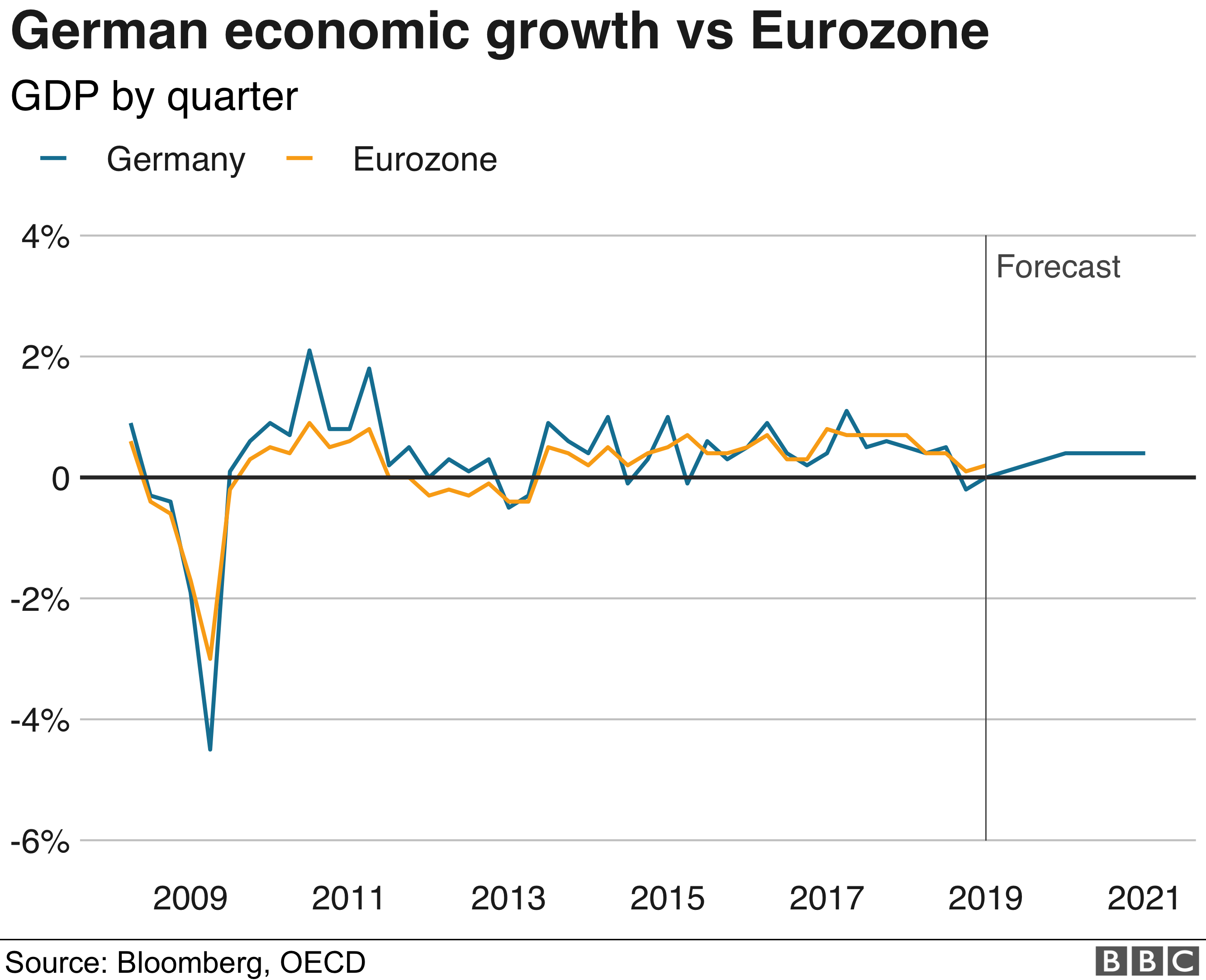 Germany S Economy Should We Be Worried Bbc News
Germany S Economy Should We Be Worried Bbc News
The economic situation in Germany was better from 1924 until 1929 when the disastrous effects of Great Depression jetted in.
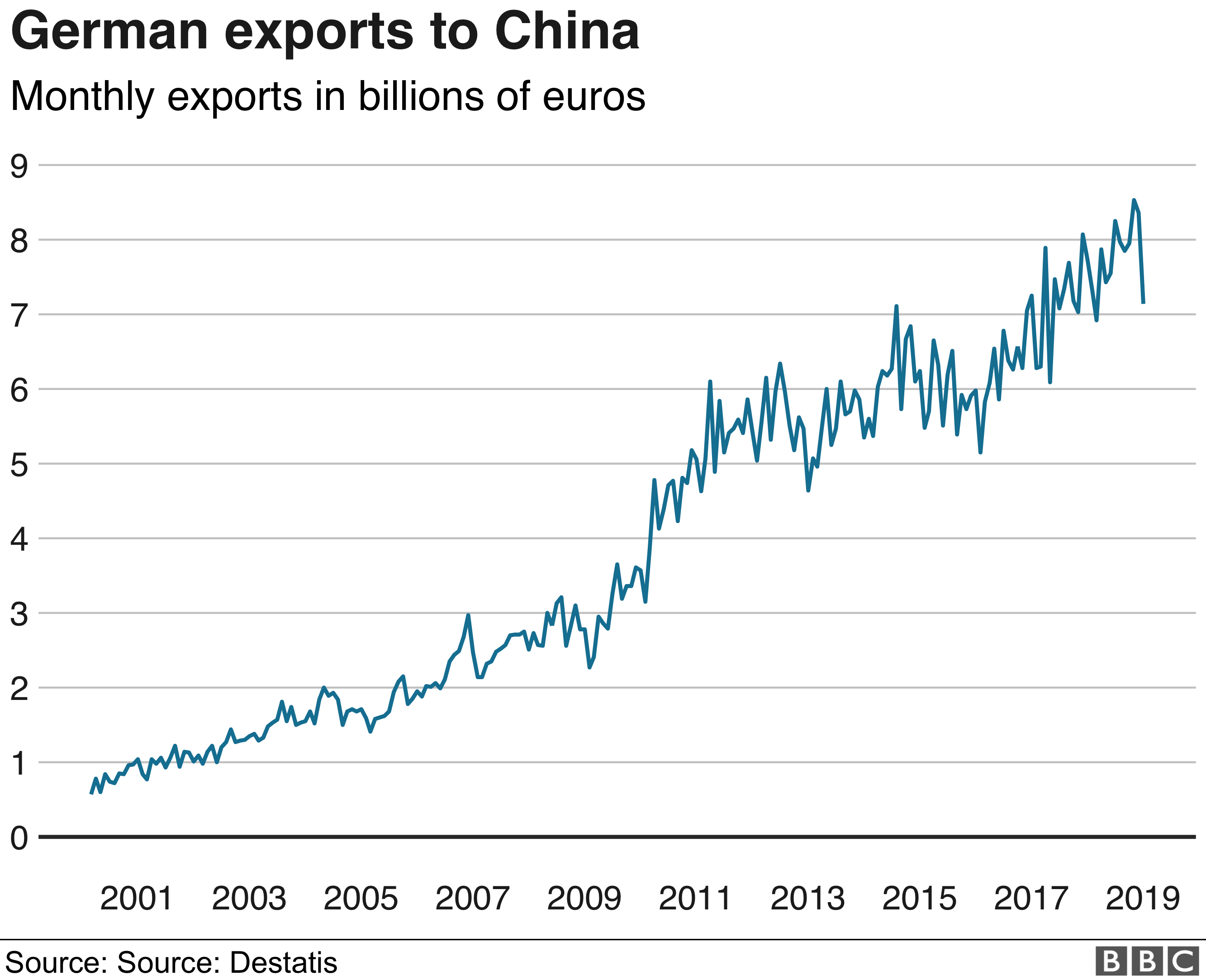
German unemployment rate great depression. Others lost their savings as banks folded. By the time Hitler became Chancellor in January 1933 one in three Germans were unemployed with the. By 1936 the depression was substantially over in Germany far from finished in the United States In fact the jobless rate in the United States remained high until the stimulation of large-scale war production took hold.
Hyperinflation affected the German Papiermark the currency of the Weimar Republic between 1921 and 1923 primarily in 1923It caused considerable internal political instability in the country the occupation of the Ruhr by France and Belgium as well as misery for the general populace. At the end of 2019 the unemployment rate in the German capital was 77 percent. In December 2020 it was 101 percent.
Desperate for capital the United States began to recall loans. Unemployment hit millions of Germans as companies shut down or downsized. Just like any other financial crisis the Great Depression had severe economic consequences especially in the United States and Germany which were largely affected by high unemployment rates in the 1930s.
The fortunes of the National Socialist German Workers Party changed with the Wall Street Crash in October 1929. 5 Unfortunately this couldnt last and in 1929 Germanys unemployment rate had increased by an average of 35 percent from the previous year. One private analytics firm Xerfi estimates that the rate will rise to 96 percent this.
The United States was an extremely significant example of this. To put the above given figures into perspective the average rate of unemployment in the US during the economic recession of 2002 was 5 and the current unemployment rate in spite of the economic turmoil stands at 83. The effects of the COVID-19 crisis are particularly evident in Berlin.
By 1928 unemployment had fallen to 84 per cent of the workforce. The unemployment rate falls during the expansion phase of the business cycle. The German people gradually gained a new faith in their democratic system and began to find the extremist solutions proposed by people such as Adolf Hitler unattractive.
Germanys experience of the Great Depression was exceptionally severe. Was hit by the great depression they immediately sought to get the loans which they had made to German paid back. Between the summer of 1929 and early 1932 German un-employment rose from just under 13 million to over 6 million corre-sponding to a rise in the unemployment rate from 45 percent of the la-bor force to 24 percent.
President Trump speaks with German Chancellor Angela Merkel on Aug. 26 2019 during a. Over the winter of 1929-30 the number of unemployed rose from 14 million to over 2 million.
Unemployment during the Great Depression As an important economic indicator during the period of 1929-1932 the rate of unemployment was the following. Following a seasonal upswing in labor demand. During the war the working class made up the largest percentage of Germanys population at around 70 percent.
But as in Germany the payoff will be that French unemployment increases will probably be fairly limited. Germany experienced hyperinflation in 1923 and chronic high unemployment throughout the 1920s as a result of the inability of the governemtn to cope with the problems of Germany effectively. Even as late as March 1940 the US unemployment rate was still almost 15 percent of the work force.
The lowest unemployment rate was 12 in 1944. When the unemployment rate jumped in 1930 as a result of the onset of the Great Depression the support for the Weimar Republic drained away. This in addition to all of Germanys other problems practically caused the German economy to collapse.
The Great Depression was particularly severe in Germany which had enjoyed five years of artificial prosperity propped up by American loans and goodwill.
 Chart Showing Prices Of German Products During Hyperinflation Teaching History Teacher Boards German History
Chart Showing Prices Of German Products During Hyperinflation Teaching History Teacher Boards German History
 One Chart Shows How Obama S Job Performance Compares With His Predecessors The Washington Post Obama Job Chart
One Chart Shows How Obama S Job Performance Compares With His Predecessors The Washington Post Obama Job Chart
 Crunch Time Financial Markets Chart Crunch
Crunch Time Financial Markets Chart Crunch
 Taking Europe S Pulse Economy Europe Guide
Taking Europe S Pulse Economy Europe Guide
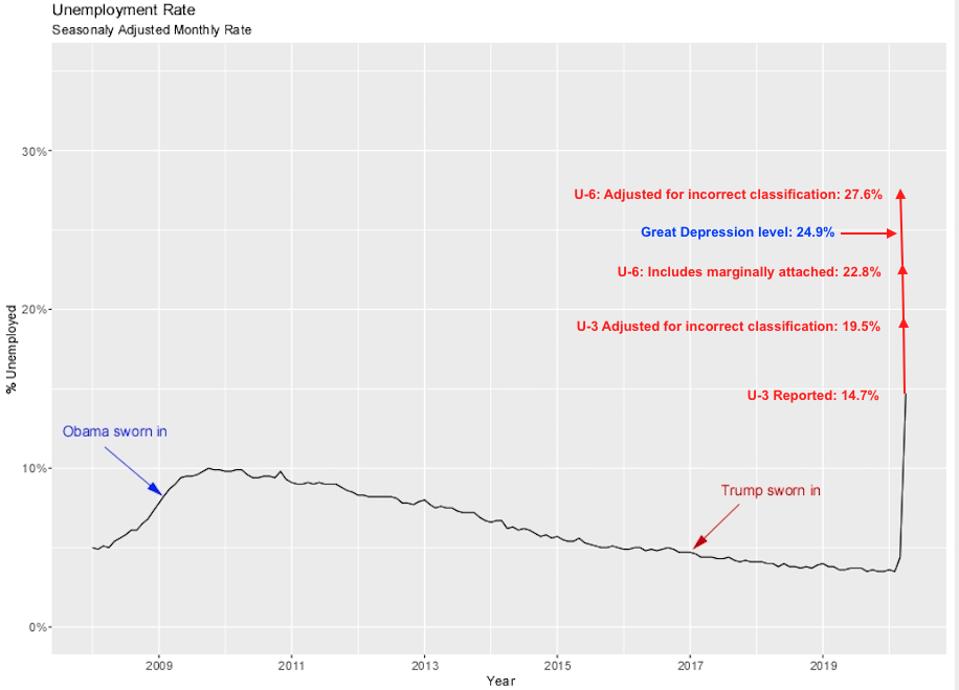 3 Reasons Unemployment Is Already At Great Depression Levels
3 Reasons Unemployment Is Already At Great Depression Levels
 11 Maps And Charts To Challenge Your Perceptions Of Europe Learning Italian How To Speak Italian Learn Another Language
11 Maps And Charts To Challenge Your Perceptions Of Europe Learning Italian How To Speak Italian Learn Another Language
 European Economic Guide Belgium Germany Europe Economy
European Economic Guide Belgium Germany Europe Economy
 Imports Versus Investments Investing Millennial Trends
Imports Versus Investments Investing Millennial Trends
 Germany S Economy Should We Be Worried Bbc News
Germany S Economy Should We Be Worried Bbc News
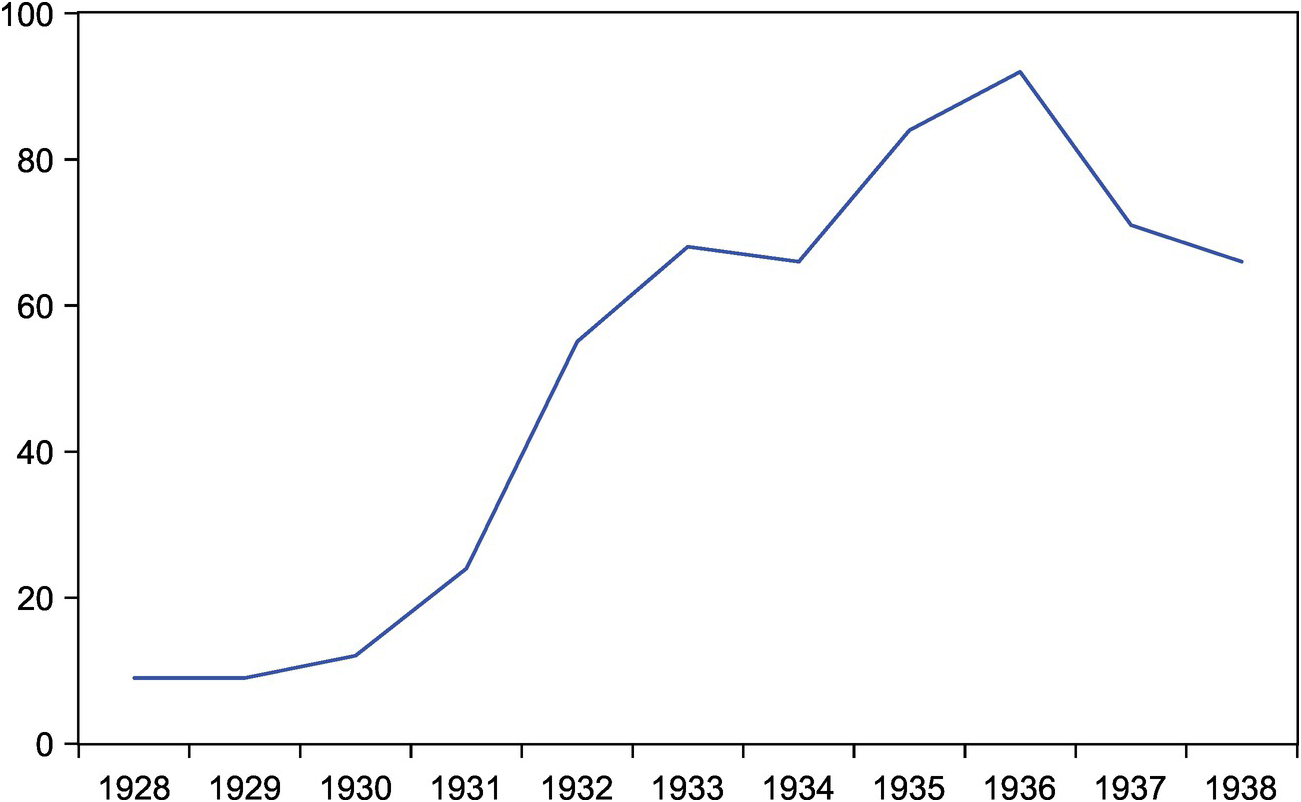 From The Great Depression To World War Ii 1929 1945 Chapter 5 Swiss Monetary History Since The Early 19th Century
From The Great Depression To World War Ii 1929 1945 Chapter 5 Swiss Monetary History Since The Early 19th Century
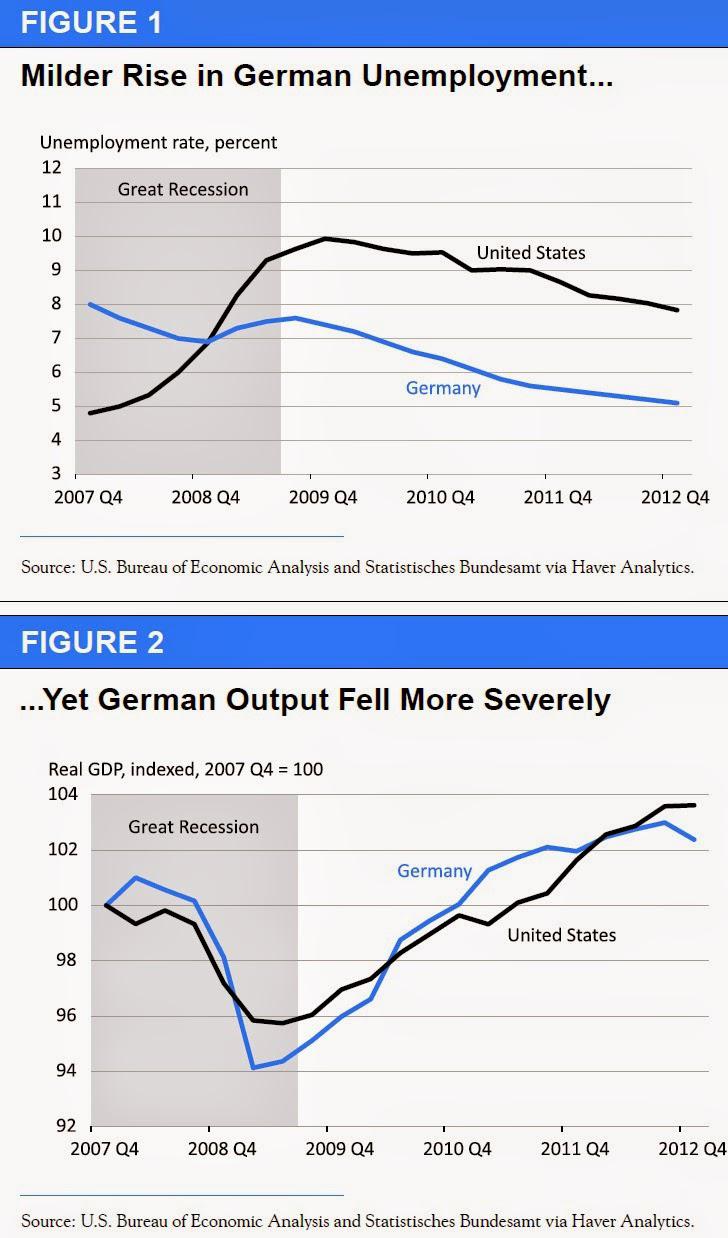 How Did Germany Limit Unemployment In The Recession Seeking Alpha
How Did Germany Limit Unemployment In The Recession Seeking Alpha
 How Did Germany Limit Unemployment In The Recession Seeking Alpha
How Did Germany Limit Unemployment In The Recession Seeking Alpha
 The Great Depression In Germany
The Great Depression In Germany
 Here Are The Countries With The Most U S Retirees Collecting Social Security Marketwatch Social Security Benefits Retirement Social Security
Here Are The Countries With The Most U S Retirees Collecting Social Security Marketwatch Social Security Benefits Retirement Social Security
 This Graph Shows The Value Of One Gold Mark From 1918 To 1924 On The 30th Nov 1923 1 Gold Mark Was Worth 1 000 000 000 000 Graphing Economics Infographic
This Graph Shows The Value Of One Gold Mark From 1918 To 1924 On The 30th Nov 1923 1 Gold Mark Was Worth 1 000 000 000 000 Graphing Economics Infographic
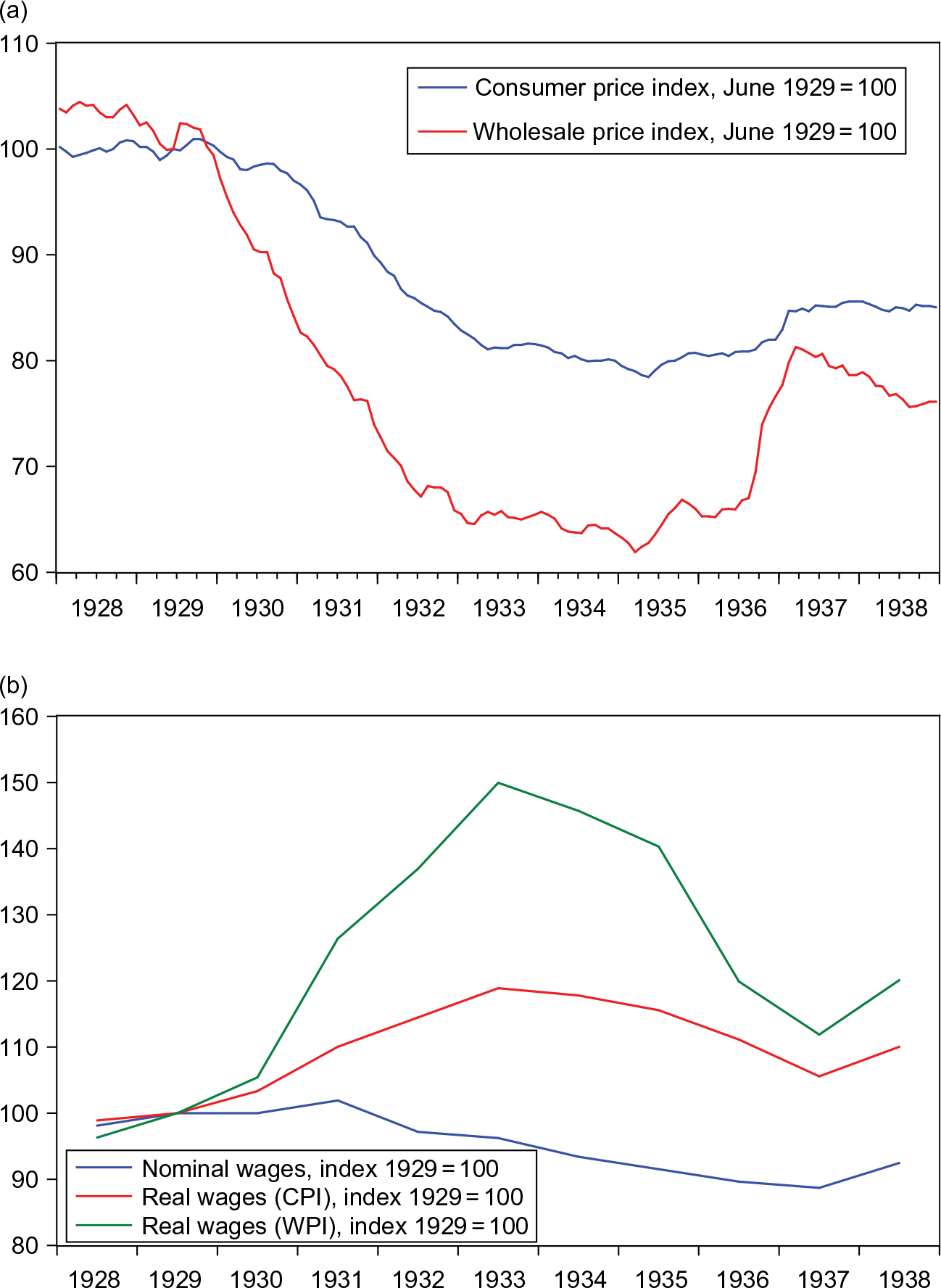 From The Great Depression To World War Ii 1929 1945 Chapter 5 Swiss Monetary History Since The Early 19th Century
From The Great Depression To World War Ii 1929 1945 Chapter 5 Swiss Monetary History Since The Early 19th Century



Post a Comment for "German Unemployment Rate Great Depression"