Unemployment Definition In Macroeconomics
On a national level unemployment is caused by a slowing economy. In addition the purchasing power of these workers is lost which can lead to unemployment for yet other workers.
 9 Secrets About Micro And Macro Economic Models That Has Never Been Revealed For The Past 9 Years Micro A Economic Model Sharing Economy Managerial Economics
9 Secrets About Micro And Macro Economic Models That Has Never Been Revealed For The Past 9 Years Micro A Economic Model Sharing Economy Managerial Economics
When unemployment is high the number of people looking for work significantly exceeds the number of jobs available.

Unemployment definition in macroeconomics. Unemployment rate dropped from 80 to 67 and by the close of 2015 it had fallen to 50At a glance the changes between the percentages may seem small. Unemployment represents the number of people in the work force who want to work but do not have a job. Unemployment occurs when someone could work and wants to work but is unable to find employment.
Workers are considered unemployed if they currently do not work despite the fact that they are able and willing to do so. Included in this group are those people in the workforce who are working but do not have an appropriate job. When the labor market is in equilibrium employment is at the natural level and the unemployment rate equals the natural rate of unemployment.
Topics include cyclical seasonal frictional and structural unemployment. Usually measured by the unemployment rate which is dividing the number of unemployed people by the total number of people in the workforce. In economics unemployment occurs when people are without work while actively searching for employment.
Unemployment is lack of full utilization of resources and eats up the production of the economy. Frictional unemployment naturally occurs even in a growing stable economy. The unemployment rate is defined as the percentage of unemployed workers in the total labor force.
Unemployment occurs when a person who is actively searching for employment is unable to find work. Unemployment umemployment rate 51 hai na kh 445 according to Awais according to the OECD Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development is persons above a specified age usually 15 not being in paid employment or self-employment but. Cyclical unemployment is the impact of economic recession or expansion on the total unemployment rate.
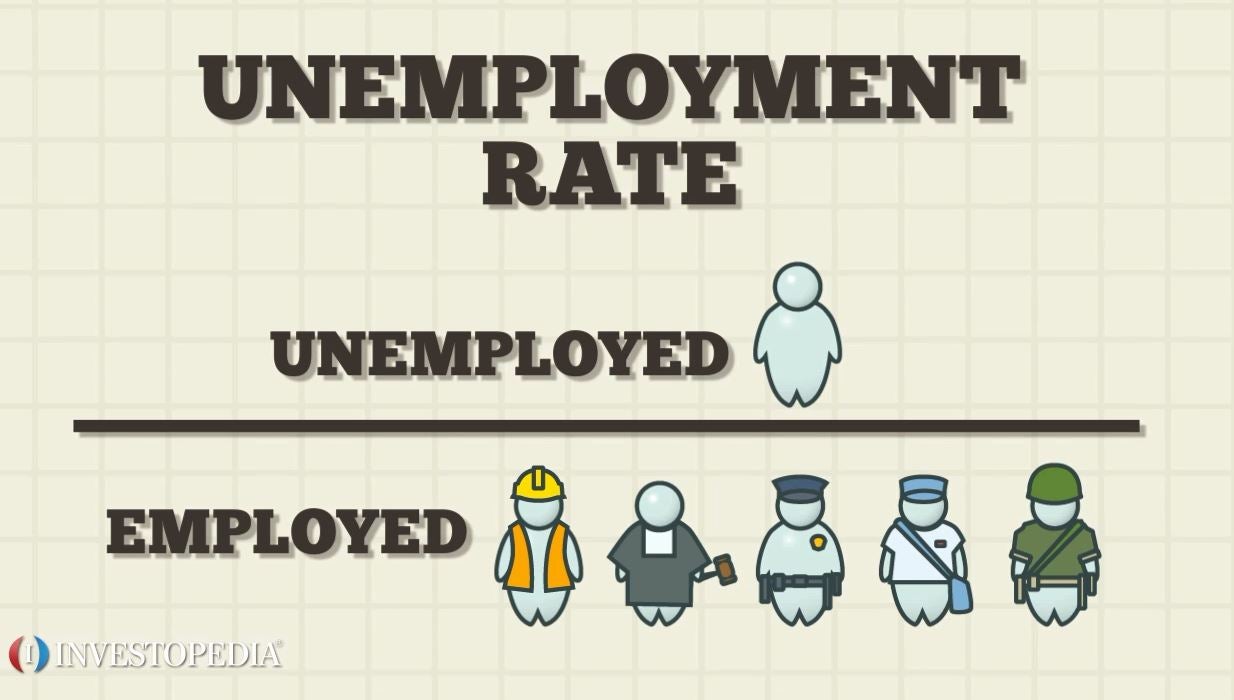
Workers choosing to leave. Unemployment is a term referring to individuals who are employable and actively seeking a job but are unable to find a job. The unemployment rate is a percentage and calculated by dividing the number of unemployed individuals by the number of all currently employed individuals in the labor force.
The total labor force consists of. It is generally stated as a percentage. Frictional unemployment is the result of voluntary employment transitions within an economy.
Unemployment is highly and negatively correlated with the productivity of the economy. A recent report might have said for example from January 2013 to December 2013 the US. Unemployment is typically described in newspaper or television reports as a percentage or a rate.
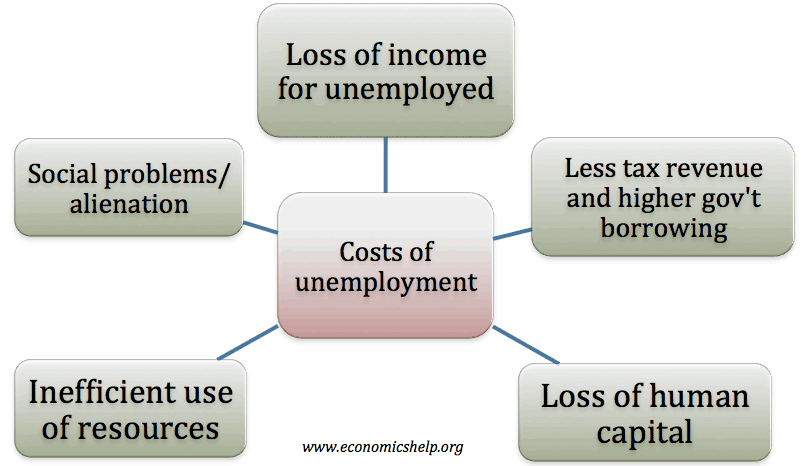
When workers are unemployed they their families and the country as a whole lose. Unemployment is often used as a measure of the health of. If a mother left work to bring up a child or if someone went into higher education they are not working but would not be classed as unemployed as they are not actively seeking employment.
Even if employment is at the natural level the economy will experience frictional and structural unemployment. Those who dont have a job but are available for work and have looked for work in the past four weeks. Workers and their families lose wages and the country loses the goods or services that could have been produced.
214 Unemployment rate The unemployment rate can be mathematically defined as the total unemployed divided by the labour force which is the sum total of employed and the unemployed. In this lesson summary review and remind yourself of the key terms and calculations used in measuring unemployment the labor force the unemployment rate the labor force participation rate and the natural rate of unemployment. The unemployment rate is the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed.
Structural unemployment is a longer-lasting form of unemployment caused by fundamental shifts in an economy and exacerbated by extraneous factors such as technology competition and government. Unemployment is defined as a situation where someone of working age is not able to get a job but would like to be in full-time employment. Cyclical unemployment generally rises during recessions and falls during economic expansions.
In other words the supply of labor is greater than the demand for it. Unemployment management is one of the toughest jobs of every government in the world. The Bureau of Labor Statistics BLS has a specific definition of unemployment.
Unemployment refers to the share of the labor force that is without work but available for and seeking employment.
 Deflation Infographic One Minute Video Teaching Economics Economics Lessons Business And Economics
Deflation Infographic One Minute Video Teaching Economics Economics Lessons Business And Economics
 This Is Why Explain Nature And Scope Of Macro Economics Is So Famous Explain Nature And Scope Of Macro Economic Economics Economy Today Economic Environment
This Is Why Explain Nature And Scope Of Macro Economics Is So Famous Explain Nature And Scope Of Macro Economic Economics Economy Today Economic Environment
 Five Fantastic Vacation Ideas For Measures Of Economic Development Measures Of Economic Development Https Economic Development Human Development Development
Five Fantastic Vacation Ideas For Measures Of Economic Development Measures Of Economic Development Https Economic Development Human Development Development
 Business Cycle Poster Project Macroeconomy Policymaking And The Business Cycle Google Classroom Activities Economics Lessons Economic Research
Business Cycle Poster Project Macroeconomy Policymaking And The Business Cycle Google Classroom Activities Economics Lessons Economic Research
 9 Advantages Of How Hard Is Macro And Micro Economics And How You Can Make Full Use Of It How Hard Is Macro And Mic Micro Economics Economics Macro And Micro
9 Advantages Of How Hard Is Macro And Micro Economics And How You Can Make Full Use Of It How Hard Is Macro And Mic Micro Economics Economics Macro And Micro
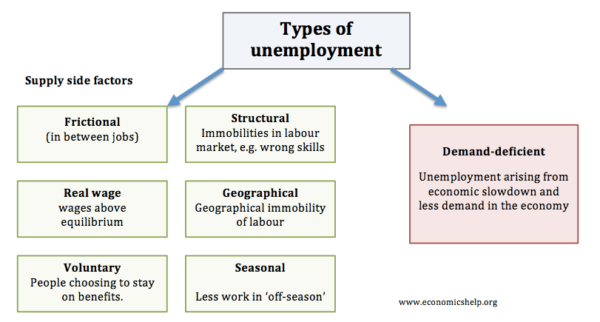 Definition Of Unemployment Economics Help
Definition Of Unemployment Economics Help
 All You Need To Know About Economic Progress Meaning Economic Progress Meaning Https Macro Economic Com All You Need To Meant To Be Economy Today Progress
All You Need To Know About Economic Progress Meaning Economic Progress Meaning Https Macro Economic Com All You Need To Meant To Be Economy Today Progress
 Understand The Background Of Microeconomics Examples Now Microeconomics Examples Https Macro Economic Com U Economics Lessons Macroeconomics Economic Model
Understand The Background Of Microeconomics Examples Now Microeconomics Examples Https Macro Economic Com U Economics Lessons Macroeconomics Economic Model
 8 Economic Factors Affecting Education System Tips You Need To Learn Now Economic Factors Affecting Education Syste Education System Education Economic Model
8 Economic Factors Affecting Education System Tips You Need To Learn Now Economic Factors Affecting Education Syste Education System Education Economic Model
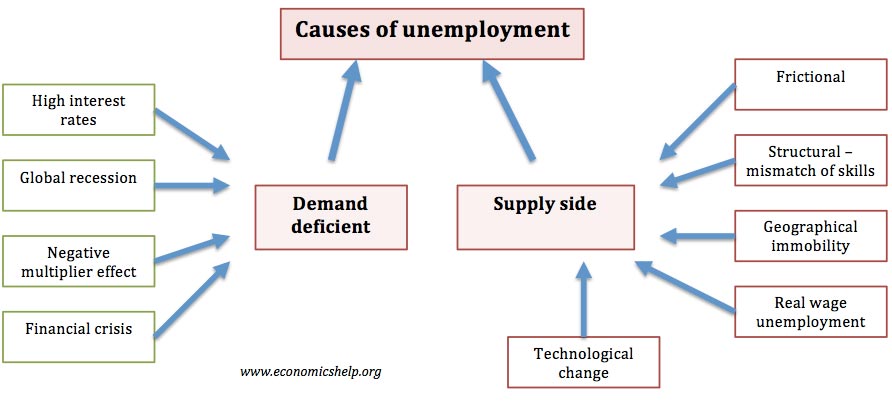 Causes Of Unemployment Economics Help
Causes Of Unemployment Economics Help
 Distinguish Between Price Elasticity And Income Elasticity Of Demand Pediaa Com Economics Notes Economics Lessons Teaching Economics
Distinguish Between Price Elasticity And Income Elasticity Of Demand Pediaa Com Economics Notes Economics Lessons Teaching Economics
 Note Taking Economics Lessons Economics Notes Study Notes
Note Taking Economics Lessons Economics Notes Study Notes
 Five Solid Evidences Attending Economies Of Scale Example Is Good For Your Career Development Economies Of Scal Economies Of Scale Economy Career Development
Five Solid Evidences Attending Economies Of Scale Example Is Good For Your Career Development Economies Of Scal Economies Of Scale Economy Career Development
 What Is Behavioural Economics Infographic B2b International Behavioral Economics Teaching Economics Economics Lessons
What Is Behavioural Economics Infographic B2b International Behavioral Economics Teaching Economics Economics Lessons
 10 Taboos About How Is Micro And Macro Economics Related You Should Never Share On Twitter How Is M Economics Notes Economic Environment Managerial Economics
10 Taboos About How Is Micro And Macro Economics Related You Should Never Share On Twitter How Is M Economics Notes Economic Environment Managerial Economics
 Principles Of Macroeconomics Lecture 5 Unemployment Ppt Download
Principles Of Macroeconomics Lecture 5 Unemployment Ppt Download

Post a Comment for "Unemployment Definition In Macroeconomics"