Unemployment Great Depression Germany
Unemployment was the result of a number of factors during the Great Depression. The most obvious consequence of this collapse was a huge rise in unemployment.
 Great Depression Holocaust Encyclopedia
Great Depression Holocaust Encyclopedia
The Great Depression was a long and extensive economic crisis affecting most developed nations in the early and mid-1930s.
Unemployment great depression germany. Germany began creating transportation projects modernization of power plants and gas works. The Great Depression. By 1928 unemployment had fallen to 84 per cent of the workforce.
The Great Depression was a severe worldwide economic depression that took place mostly during the 1930s beginning in the United StatesThe timing of the Great Depression varied across the world. Unemployment and the Great Depression in Weimar Germany. By 1925 it had risen to almost.
The Great Depression was a serious economic crisis that facilitated high unemployment rates in Germany and America. Complete collapse of the stock market worldwide. Cut-back business and government expenditures.
The New and the Old Woman on the Dark Side of the Golden Twenties in Germany. Germanys experience of the Great Depression was exceptionally severe. Between the summer of 1929 and early 1932 German un-employment rose from just under 13 million to over 6 million corre-sponding to a rise in the unemployment rate from 45 percent of the la-bor force to 24 percent.
In 1929 as the Wall Street Crash led to a worldwide depression. DPetzina - Physicians in Crisis at the End of the Weimar Republic. MHKater - Unemployment also Hits Women.
The unemployment rate in Germany Austria and Poland rose to 20 while output fell by 40. The elimination of unemployment in Germany during the Great Depression without inflation and with initial reliance on essential civilian activities was a signal accomplishment. The notion that Hitler could do no good extends to his economics as it does more plausibly to all else.
Without these loans German industry collapsed and a depression began. The Great Depression led to unemployment in the USA and many other countries including Germany. The fortunes of the National Socialist German Workers Partychanged with the Wall Street Crashin October 1929.
Over the winter of. The Great Depression severely affected Central Europe. The Great Depression was particularly severe in Germany which had enjoyed five years of artificial prosperity propped up by American loans and goodwill.
The unemployed people in these two nations engaged in casual jobs avoided some luxurious items and activities and some even engaged in stealing as coping strategies to survive the great depression. The Great Depression in Germany The German economy was very closely tied to the one in America and when the Wall Street collapsed the German economy followed in tow. Unemployment and the Great Depression in Weimar Germany.
Between the summer of 1929 and early 1932 German unemployment rose from just under 13 million to over 6 million corresponding to a rise in the unemployment rate from 45 percent of the labor force to 24 percent. By November 1949 every European country had increased tariffs or introduced import quotas. The German people gradually gained a new faith in their democratic system and began to find the extremist solutions proposed by people such as Adolf Hitlerunattractive.
Germanys experience of the Great Depression was exceptionally severe. Germany suffered more than any other nation as a result of the recall of US loans which caused its economy to. FREE shipping on qualifying offers.
PDStachura - The Extent and Causes of Unemployment in the Weimar Republic. There was far-flung unemployment reaching as high as 25 since every industrial sector was in bad shape. It has rarely been praised and not much remarked.
Was spending approximately 205 per resident. These were all used to battle the increasing unemployment Social spending was rising at an unbelievable rate. The Development of Unemployment in Modern German History.
Low credit availability that added to debt by borrowing. Unemployment Great Depression and Germany Around 90 of the restitution disbursements of Germany were invalidated in 1932. In most countries it started in 1929 and lasted until the late 1930s.
Table of Contents Notes on the Contributors - Introduction. It was the longest deepest and most widespread depression of the 20th century. Drought conditions that ravaged agricultural regions worldwide.
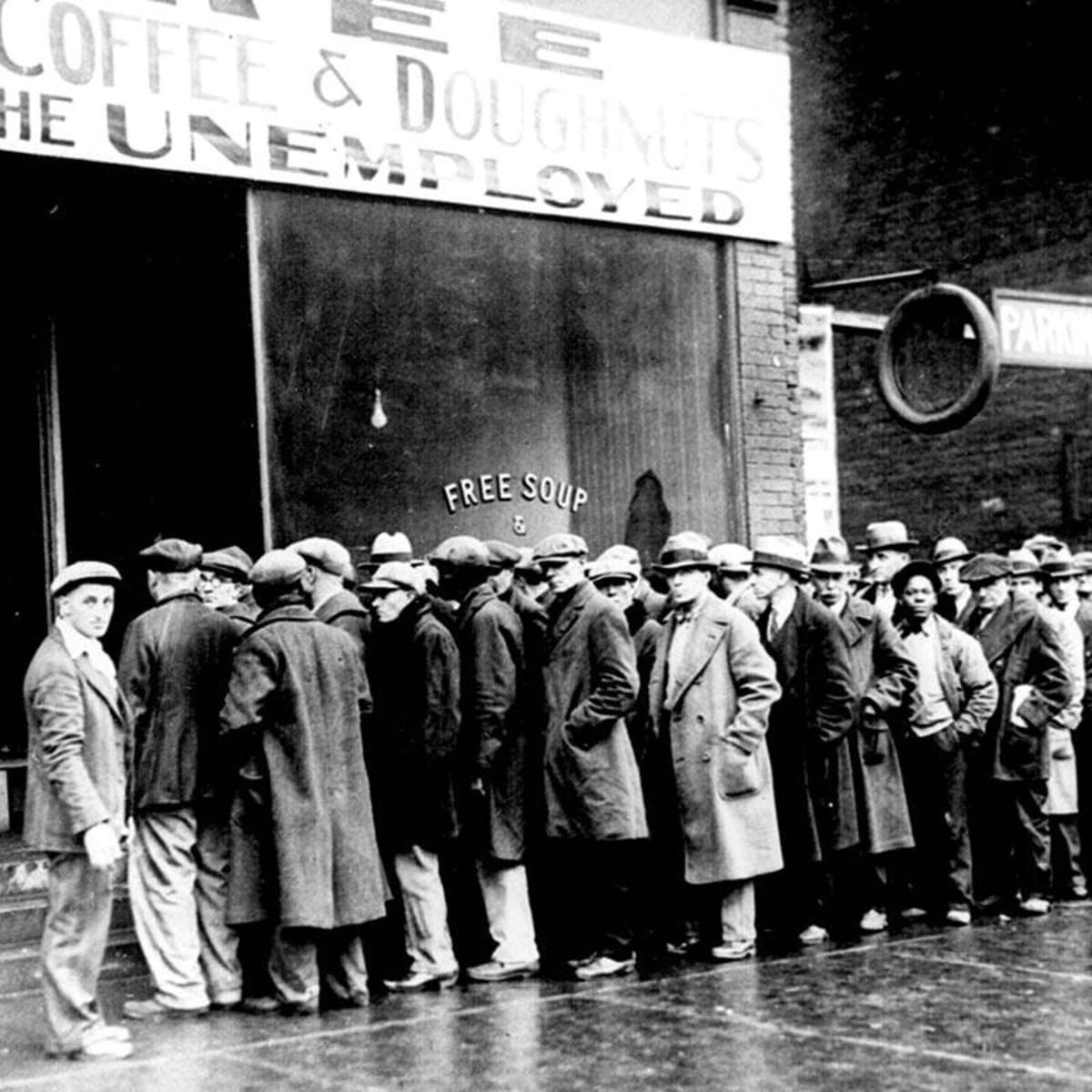
Unemployed people queue in Berlin during the Depression. Some of the trigger factors included. Following a seasonal upswing in labor demand.
The Great Depression is commonly used as an.
 Unemployment In 1930s Unprecedentedly High
Unemployment In 1930s Unprecedentedly High
 Unemployment In Interwar Germany An Analysis Of The Labor Market 1927 1936 The Journal Of Economic History Cambridge Core
Unemployment In Interwar Germany An Analysis Of The Labor Market 1927 1936 The Journal Of Economic History Cambridge Core
The Great Depression Miss Migliore S Classroom
Chart German Unemployment And Nazi Vote
 Comparing U S Japanese And German Fiscal Responses To Covid 19 Center For Strategic And International Studies
Comparing U S Japanese And German Fiscal Responses To Covid 19 Center For Strategic And International Studies
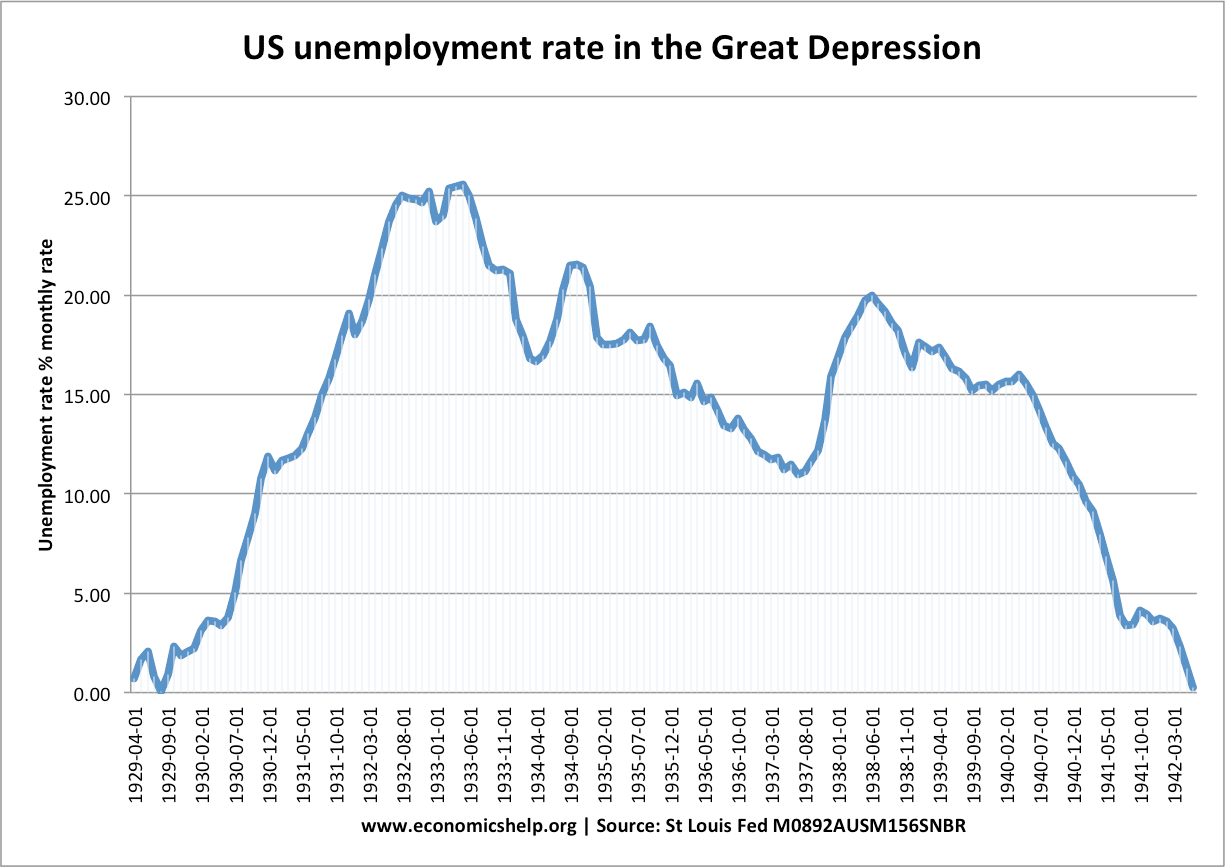 List Of Recessions In Uk And Us Economics Help
List Of Recessions In Uk And Us Economics Help
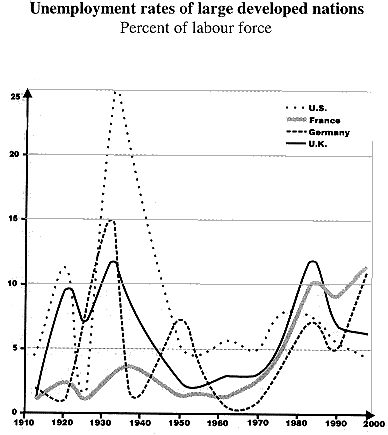 Unemployment Risks And Reactions Nikolai Genov Ed Unesco Most Fes Teil 3
Unemployment Risks And Reactions Nikolai Genov Ed Unesco Most Fes Teil 3
Https Arkjohnkeats Org Sites Default Files Paper 203 20info 20booklet 20 20y10 Pdf
Chart German Unemployment And Nazi Vote
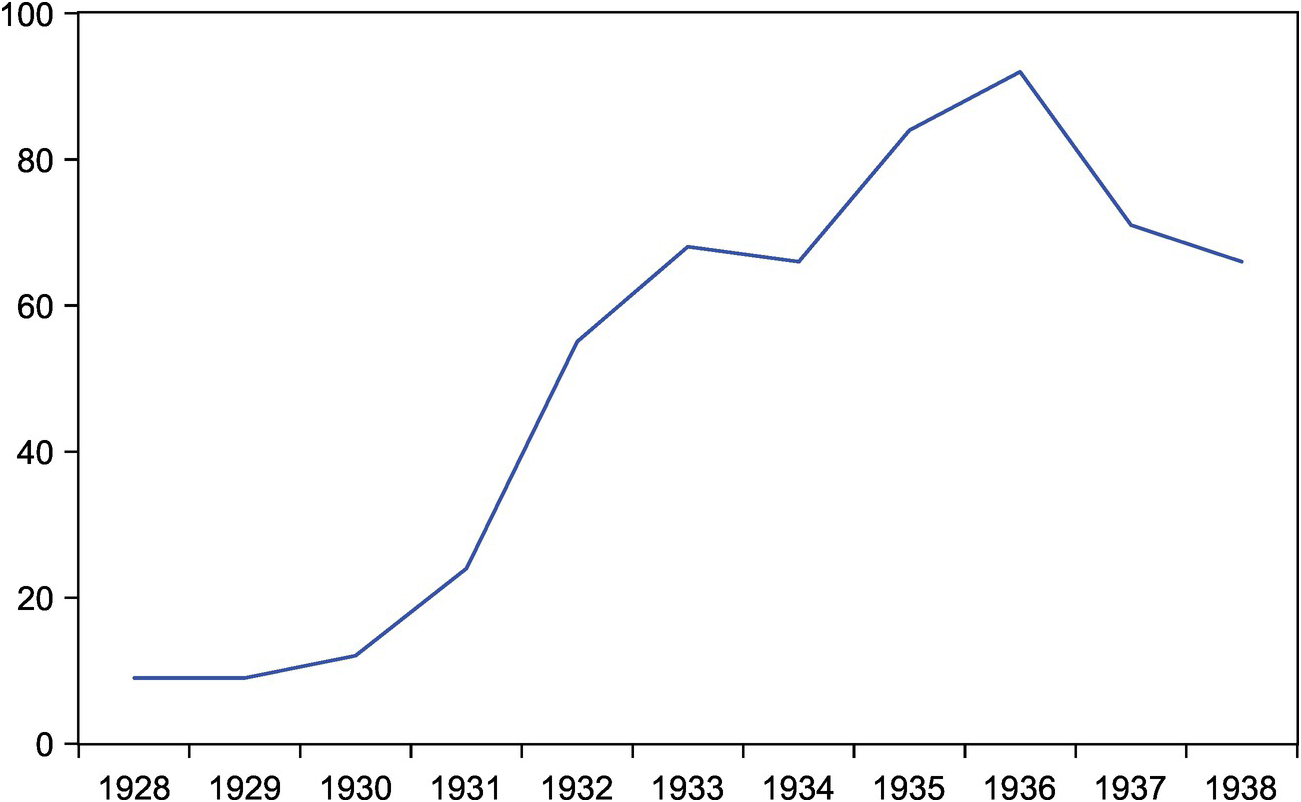 From The Great Depression To World War Ii 1929 1945 Chapter 5 Swiss Monetary History Since The Early 19th Century
From The Great Depression To World War Ii 1929 1945 Chapter 5 Swiss Monetary History Since The Early 19th Century
 The Great Depression In Germany
The Great Depression In Germany
 Great Depression Causes Effects And History Thestreet
Great Depression Causes Effects And History Thestreet
 Worse Than The 1930s Europe S Recession Is Really A Depression The Washington Post
Worse Than The 1930s Europe S Recession Is Really A Depression The Washington Post
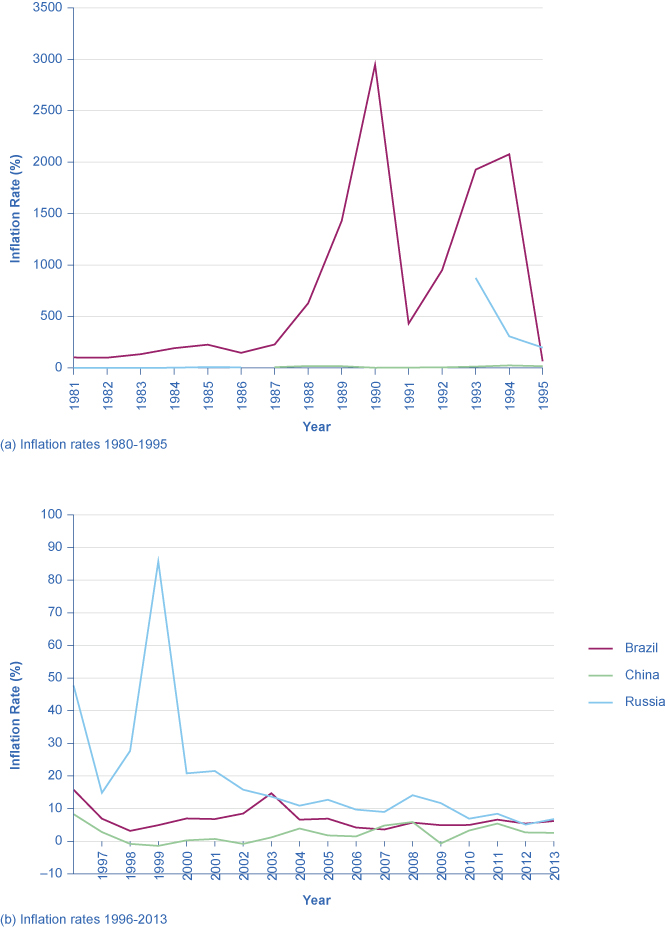 22 3 How The U S And Other Countries Experience Inflation Principles Of Economics
22 3 How The U S And Other Countries Experience Inflation Principles Of Economics
Great Depression Holocaust Encyclopedia
 The Great Depression In Germany
The Great Depression In Germany
 Historical And Current Development Of Migration To And From Germany Bpb
Historical And Current Development Of Migration To And From Germany Bpb
Weimar Germany Hyperinflation Explained
Post a Comment for "Unemployment Great Depression Germany"