Unemployment Definition Economics Class 9
Unemployment exists when a person 15 to 59 years of age is willing to work at acceptable wages cannot find a job. Additionally if a person voluntarily does not want to work he cannot be termed as unemployed.
What Is Unemployment.

Unemployment definition economics class 9. But unemployment also includes economic costs to the broader society. But if 4 people are withdrawn from it there will be no reduction in output. It is generally stated as.
8 In other words wages are higher than the laws of supply and demand would. The human costs of unemployment alone would justify making a low level of unemployment an important public policy priority. Educated unemployment as its name a person who got educated but not able to get the deserving job is called educated unemployment but let me explain suppose you hav a degree of bachelor of science and you are force to engage in job which is intended to do by a person who r illiterate or so.
Seasonal unemployment refers to the time period when the demand for labor or workforce is lower than normal under certain conditions however such a situation is only temporary and employment reverts to normal thereafter. U-3 Unemployment Rate. It measures the number of people who are jobless but actively seeking employment.
Unemployment is a term referring to individuals who are employable and actively seeking a job but are unable to find a job. When a person is actively seeking a job but is unable to get employed he is called an unemployed person. The unemployment rate is the most frequent measure of unemployment.
Unemployment is a key economic indicator because it signals the ability or inability of workers to readily obtain gainful work to contribute to the productive output of the economy. So these 4 people are actually facing disguised unemployment. When millions of unemployed but willing workers cannot find jobs an economic.
Hidden unemployment or disguised unemployment is a kind of unemployment where some people seem to be employed but are not. Many public policies can also discourage the creation of employment such as a high minimum wage high unemployment benefits and a low opportunity cost associated with terminating workers. The unemployment rate is the number of people unemployed divided by the working population or people working under labour force.
In rural areas this type of unemployment is generally found in agricultural sector like - in a family of 9 people all are engaged in the same agricultural plot. Unemployment is a situation when a person actively searches for a job and is unable to find work. Included in this group are those people in the workforce who are working but do not have an appropriate job.
Employment is the primary source of income for a person and hence it is the source of economic growth. In other words those who would like a full-time job but can only find part-time work. Unemployment represents the number of people in the work force who want to work but do not have a job.
The following are examples of seasonal unemployment. U-1 is the narrowest definition of unemployment and U-6 is the broadest measure of unemployment. This means anyone without a job who is reaching out to contacts about jobs or applying to positions.
The definition of an unemployed person is someone of working age 16 and up jobless able and available to work and actively looking for a job. The official unemployment rate is known as known as the U-3 rate or simply U3. People in the working age 15 to 59 years only can be termed unemployed if any one of them is without a gainful employment.
Notes On Unemployment - CBSE Class 9 Economics. Usually measured by the unemployment rate which is dividing the number of unemployed people by the total number of people in the workforce. Classical unemployment is also known as real wage unemployment or induced unemployment Its when wages are so high that employers cant hire all the available workers.
This basically means that on paper you can show employment but in reality too many have been hired to do a job that can be done by fewer people. Such a person is called an unemployed person. U-6 includes all classes of Unemployed even those considered marginally attached andor part-time for economic reasons.
This usually occurs when there is over-employment in a particular sector. Examples of Seasonal Unemployment. It is considered a lagging economic indicator.
Unemployment indicates the health of the economy. This definition of unemployment is specific and rigidit doesnt just include anyone who doesnt have a job.
 8 Disadvantages Of Macro Economics Variables And How You Can Workaround It Macro Economics Variables Https Macro Macroeconomics Economics Aggregate Demand
8 Disadvantages Of Macro Economics Variables And How You Can Workaround It Macro Economics Variables Https Macro Macroeconomics Economics Aggregate Demand
 The Story Of Ap Economics Macro Stagflation Has Just Gone Viral Ap Economics Macro Stagflation Https Macro Economic Com T Economics Macroeconomics Just Go
The Story Of Ap Economics Macro Stagflation Has Just Gone Viral Ap Economics Macro Stagflation Https Macro Economic Com T Economics Macroeconomics Just Go
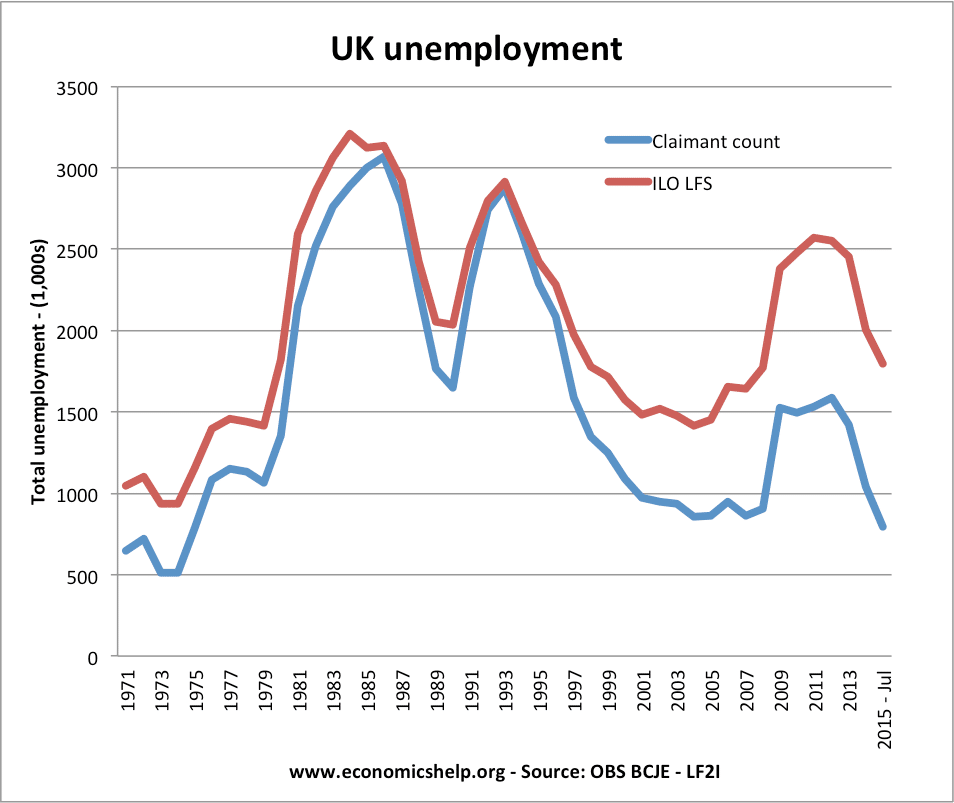 Definition Of Unemployment Economics Help
Definition Of Unemployment Economics Help
 Justmefiona Economics Lessons Economics Notes Study Notes
Justmefiona Economics Lessons Economics Notes Study Notes
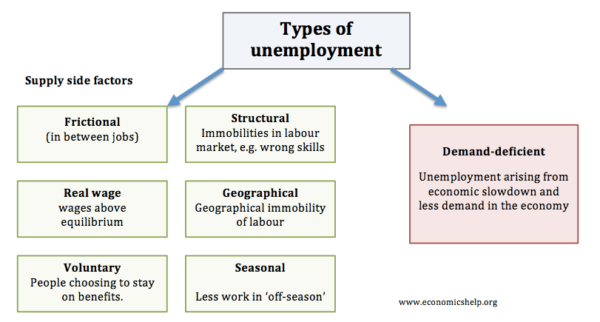 Definition Of Unemployment Economics Help
Definition Of Unemployment Economics Help
 9 Important Life Lessons Explain Economic Growth Taught Us Explain Economic Growth Https Macro Economic Com 9 Important Life Lessons Life Lessons Teaching
9 Important Life Lessons Explain Economic Growth Taught Us Explain Economic Growth Https Macro Economic Com 9 Important Life Lessons Life Lessons Teaching
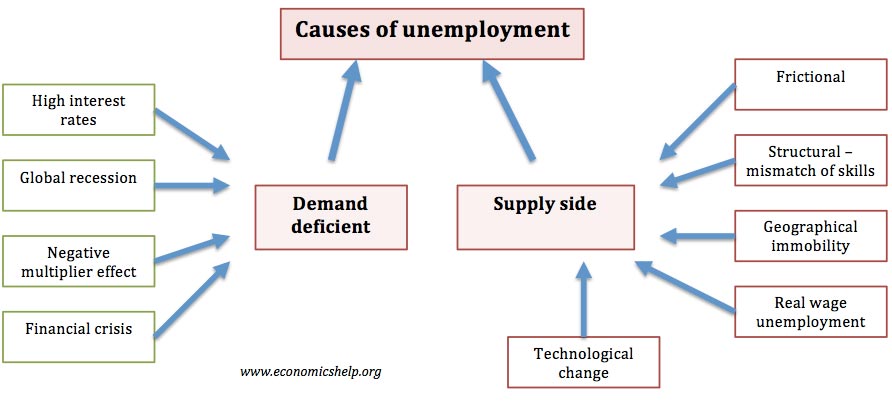 Causes Of Unemployment Economics Help
Causes Of Unemployment Economics Help
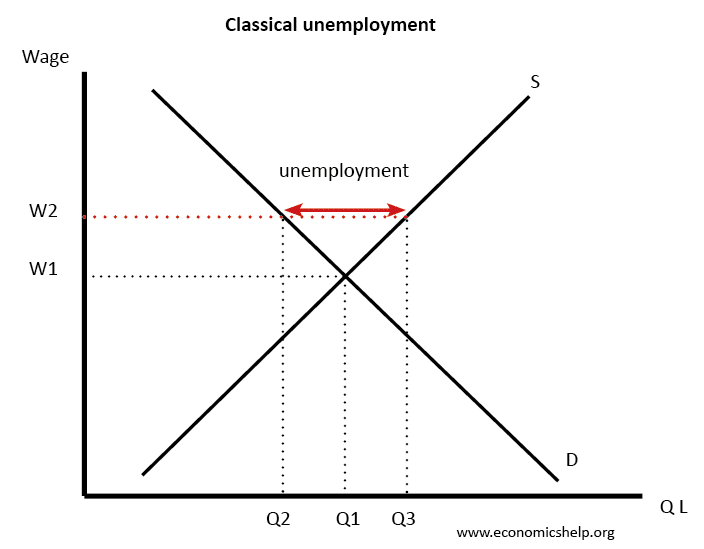 Definition Of Unemployment Economics Help
Definition Of Unemployment Economics Help
 Business Cycle Poster Project Macroeconomy Policymaking And The Business Cycle Google Classroom Activities Economics Lessons Economic Research
Business Cycle Poster Project Macroeconomy Policymaking And The Business Cycle Google Classroom Activities Economics Lessons Economic Research
/UnemploymentandGDP2008-80ffa8c6bee640208888f8cc26cb38e2.jpg) Unemployment And Recession What S The Relation
Unemployment And Recession What S The Relation
 The Teacher S Guide For Informational Text Part Of My Lesson On Supply And Demand Teaching Economics Economics Notes Economy Lessons
The Teacher S Guide For Informational Text Part Of My Lesson On Supply And Demand Teaching Economics Economics Notes Economy Lessons
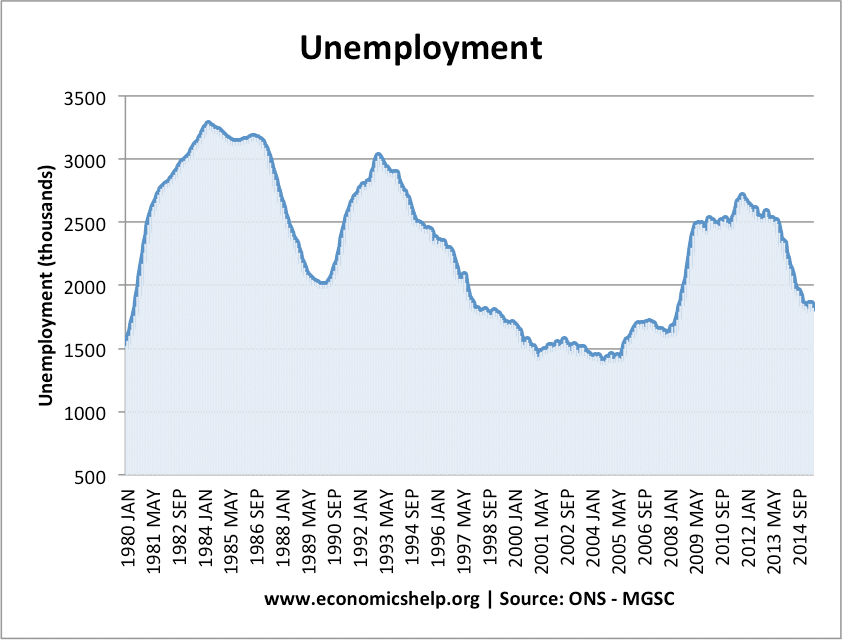 Causes Of Unemployment Economics Help
Causes Of Unemployment Economics Help
/dotdash_Final_Okuns_Law_Economic_Growth_and_Unemployment_Oct_2020-01-2e5dd7aa7c194e14a82707b84b00d1a3.jpg) Okun S Law Economic Growth And Unemployment
Okun S Law Economic Growth And Unemployment
 9 Ingenious Ways You Can Do With Compare Micro And Macro Economics Compare Micro And Macro Economics Https Macro Economics Micro Economics Economics Notes
9 Ingenious Ways You Can Do With Compare Micro And Macro Economics Compare Micro And Macro Economics Https Macro Economics Micro Economics Economics Notes
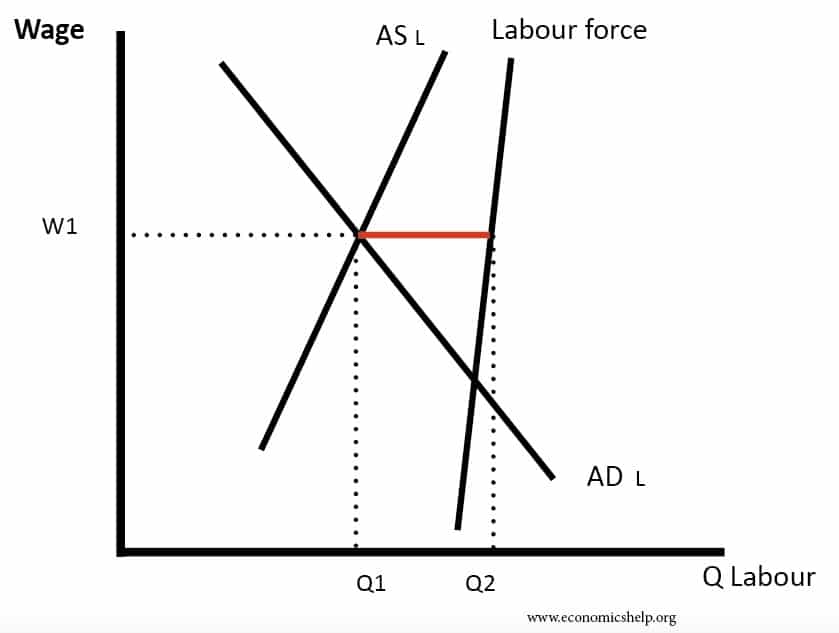 The Natural Rate Of Unemployment Economics Help
The Natural Rate Of Unemployment Economics Help
 9 Advantages Of How Hard Is Macro And Micro Economics And How You Can Make Full Use Of It How Hard Is Macro And Mic Micro Economics Economics Macro And Micro
9 Advantages Of How Hard Is Macro And Micro Economics And How You Can Make Full Use Of It How Hard Is Macro And Mic Micro Economics Economics Macro And Micro


Post a Comment for "Unemployment Definition Economics Class 9"